Since the tragic circumstances of the Grenfell disaster, designing for fire and construction material choice in all its facets has become a focus of design teams across the world. In balance, the global demand for energy efficiency and net-zero carbon pulls designers in an equally important direction.
Farrat recently held a webinar to explore these issues. Thank you to all those that attended, if you would like a certificate of attendance please email [email protected] with the name you joined the webinar with.
If you would like to access the slides from this event Click Here.
Farrat TBF – surpassing structural and fire resistance requirements
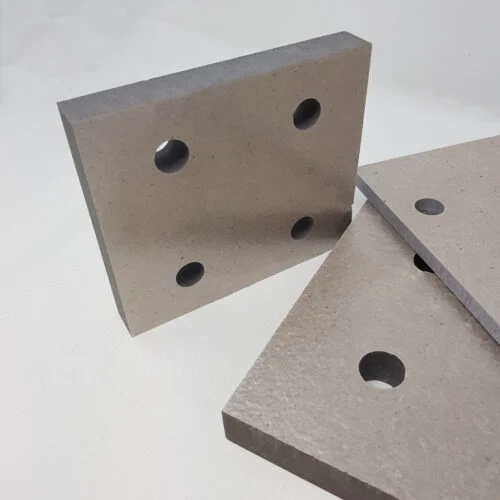
Farrat unveiled the market’s first A2 Fire Rated Structural Thermal Break ‘Farrat TBF’ in 2019, following 12 months of research and development in consultation with Salford and Manchester Universities, material scientists, and specialist raw material producers.
Farrat TBF is an A2,s1,d0 non-combustible Structural Thermal Break material designed to maintain full structural integrity in the event of a fire.
Alongside its limited combustibility, the new Farrat TBF material stands alongside the market’s best performing thermal insulators, with very high compressive strength and low thermal conductivity – preventing thermal bridges from forming between structural connections and mitigating against the risk of condensation, mould, or corrosion.
In 2020, following further investigation and enhancing the performance criteria,Farrat TBF met and exceeded the stringent structural requirements of two hour/ 550⁰C fire resistance, and in 2021 Farrat TBF was certified by the BBA, alongside our other market-leading thermal break products; Farrat TBK and Farrat TBL.
Download the datasheet for more information about Farrat TBF
Case study
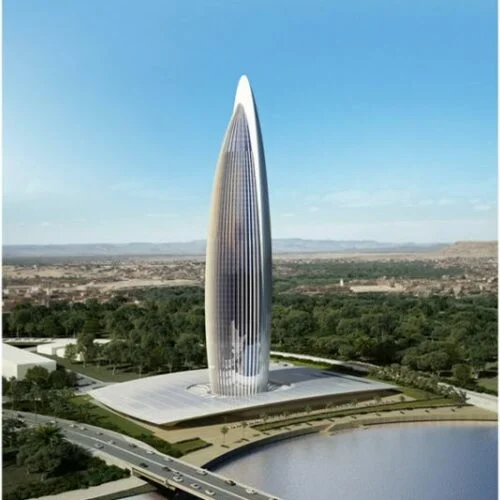
Working with an international design team to achieve the highest energy efficiency & sustainability standards, for an exciting new high-rise tower located in Morocco’s City of Light
Set to be the tallest building in Africa at 250-metres with 55 stories, Mohammed Tower IV is a new high-rise tower designed by Rafael de la Hoz & Hakim Benjelloun to resemble a rocket on its launch pad. Farrat TBF was selected as the optimal structural thermal break material for extensive use across the façade connections of Mohammed Tower, to prevent heat transfer through steel beams where the external building aspects meet the interior. Read the full case study.
To talk to Farrat about our structural A2 Fire Rated Structural Thermal Break ‘Farrat TBF’get in touch, or find out more by downloading the datasheet.
Visit our Structural Thermal Break hub for information on Farrat’s full range